# Stream Module
# Stream Intro
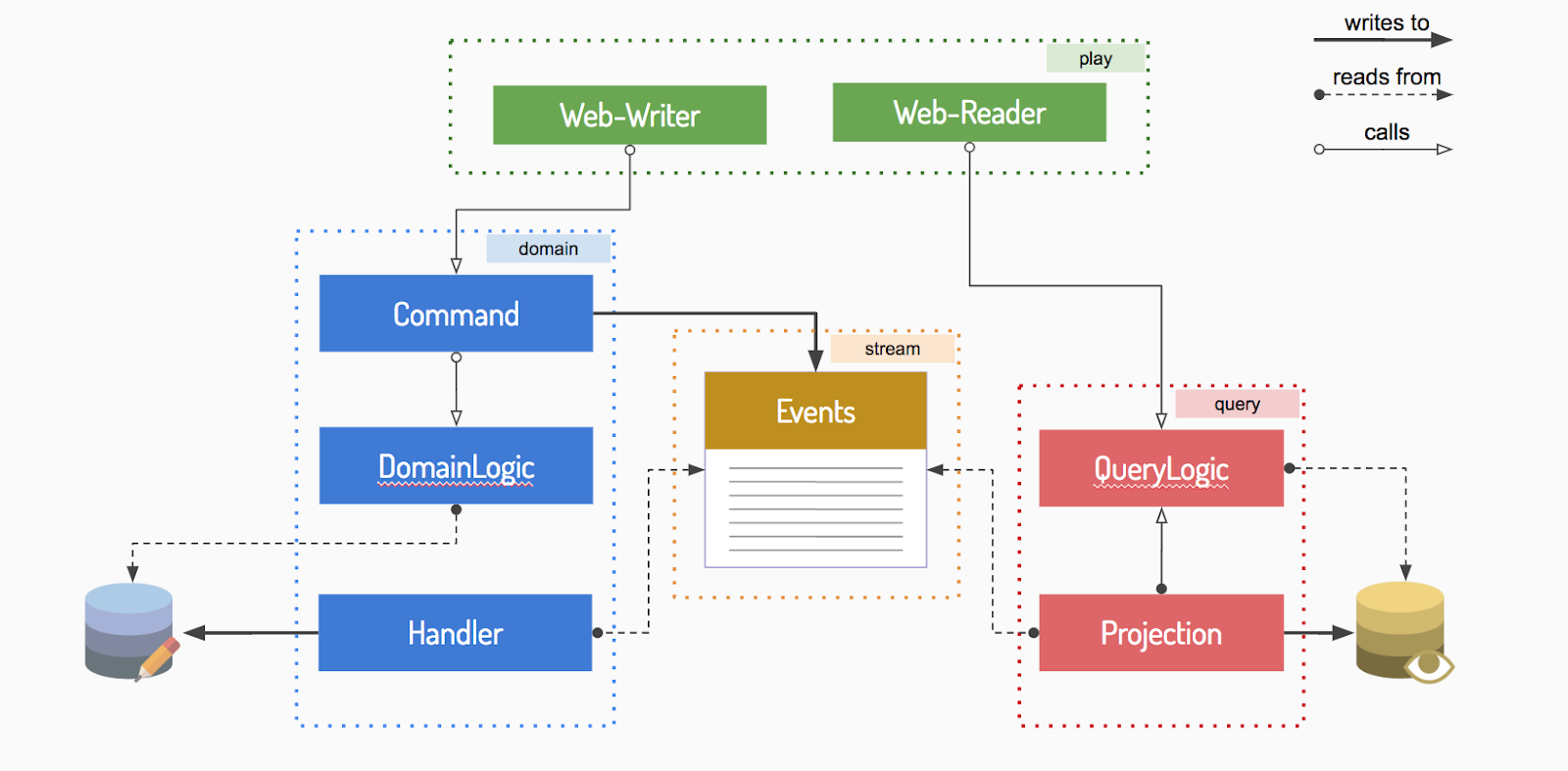
# Module Interaction
Modules interaction for an Event Driven application
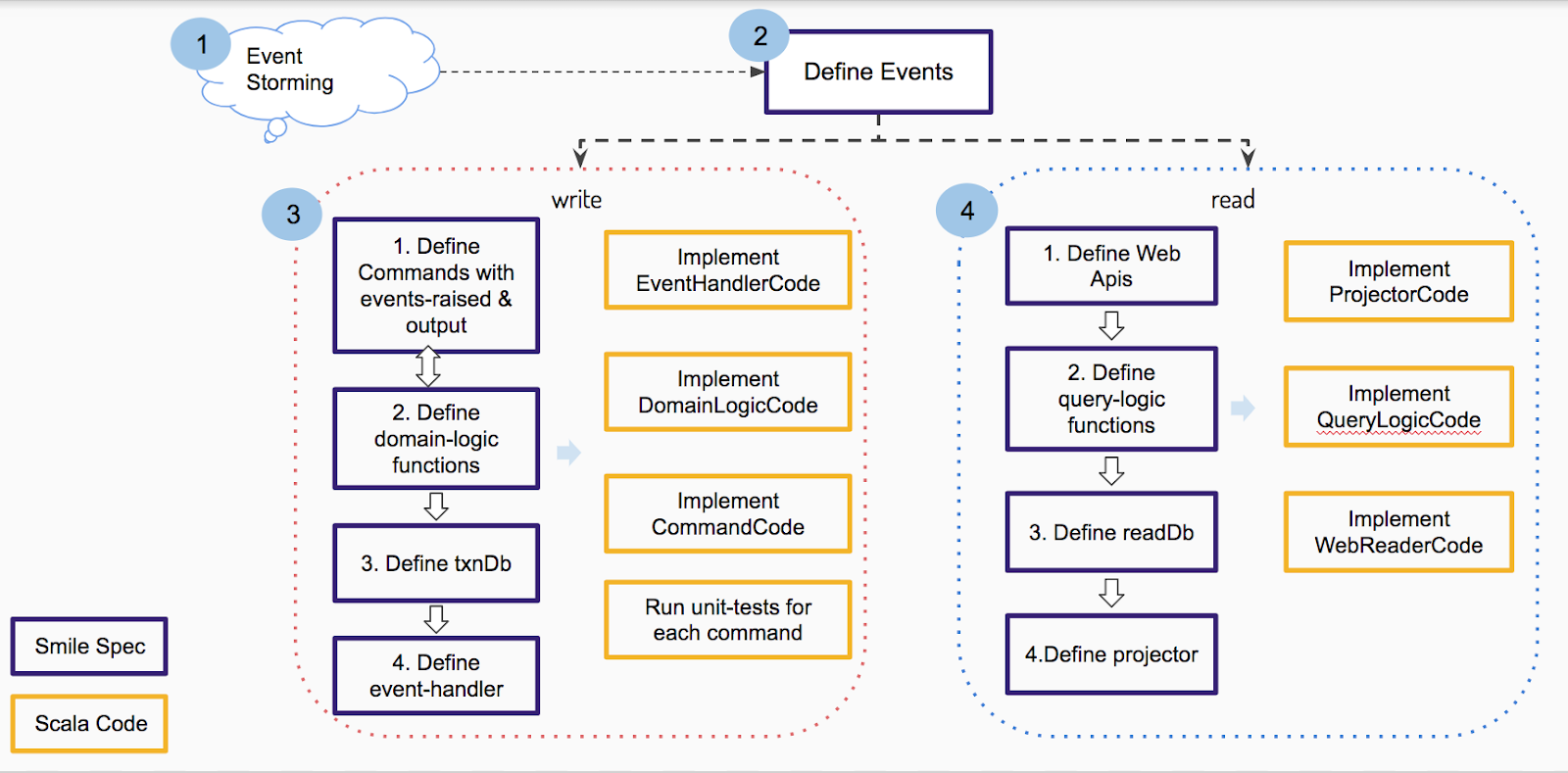
# Event based system development
Below diagram shows the developmeny cycle in event based system.
# Defining events
- List all the business events in an Event Storming session(s). Events must be in past tense, ex: CustomerCreated.
- Define a stream module where you can spec the events
stream-module LearningStream at com.metastay.leaningstream
- Run smile command & refresh project in eclipse
- Open
LearningStream.kstreamfile and define the event
event EmployeeRegistered(employeeId:Id, name:String, gender:String, experienceInMonths:Int, emailId:String, designation:String)
NOTE
event cannot have enums or composite data-types.
# Write-side Story
# Define the commands in the domain module.
- Command definition now will include the event/events it would generate rather than write to a db directly.
- Add the stream module as a dependency for domain module.
domain-module LearningDomain(LearningMongo, LearningStream) at com.metastay.learningdomain
- Run smile command.
- Open
LearningDomain.kdomainfile and define a new command set for Employee which raises events defined in LearningStream
command-set[LearningStream] Employee {
command registerEmployee{
input(name:String, gender:String, experienceInMonths:Int, emailId:String, designation:LearningData::DesignationType)
event-raised(registered:EmployeeRegistered)
output(employeeId:Id)
}
}
- Compile the code to see
EmployeeCommandSetCode.scalagenerated
# Define the domain logic functions
- Add a domain logic for Employee. Since the employee will be uniquely identified by emailId, have a function to check the uniqueness
domain-logic Employee {
function emailExists(emailId:String):Boolean
}
- Define employee domain-ref and add the pre-condition for registerEmployee command
command-set[LearningStream] Employee {
domain-logic-ref employeeDomainRef:Employee
command registerEmployee{
input(name:String, gender:String, experienceInMonths:Int, emailId:String, designation:LearningData::DesignationType)
pre{
condition emailIdMustBeUnique => !employeeDomainRef.emailExists(input.emailId) failing "Employee already registered (email exists)"
}
event-raised(registered:EmployeeRegistered)
output(employeeId:Id)
}
}
- Compile the code
# Define the transaction database
The information that is needed to implement the domain logic functions defines the transactional database content & structure. In this case all we need is the emailId of an employee in our transactionDb Create a mongo module - Add LearningTxnMongo module definition to ksmile
mongo-module LearningTxnMongo at com.metastay.learningtxnmongo
- Run smile & refresh eclipse
- Open
LearningTxnMongo.kmongo, add the Employee collection
collection Employee {
property emailId:String
}
# Define event-handlers
Identify the events that would be needed to populate the transaction db, in this case there is just one - EmployeeRegistered and it’s needed to populate the emailId.
- Open
LearningDomain.kdomainfile in eclipse - Define an event-handler for LearningStream stream
event-handler[LearningStream] Employee {
EmployeeRegistered
}
- Compile to see
EmployeeEventHandlerCode.scalaclass generated - Add LearningTxnMongo dependeny to LearningDomain, so that the event handler code can access transaction db.
domain-module LearningDomain(LearningMongo, LearningStream, LearningTxnMongo) at com.metastay.learningdomain
# Implement the event handler code
- Open
EmployeeEventHandlerCode.scalain intelliJ and implement as follows:
object EmployeeEventHandlerCode extends Employee.Group {
override def handleException(event: com.metastay.leaningstream.stream.LearningStreamEvent, context: EventContext, throwable: Throwable): Unit = {
appLogger.error(s"Employee Event Handler failed for event $event with exception: ${throwable.stackTraceString} ")
}
override def handle(event: EmployeeRegistered, context: EventContext): Unit = {
val row = EmployeeRow(_id = event.employeeId, emailId = event.emailId)
EmployeeWriter().insert(row)
}
}
- Code should compile successfully.
# Implement domain logic code
- Open
EmployeeDomainLogicCode.scalain intelliJ - Implement the emailExists method
class EmployeeDomainLogicCode extends EmployeeDomainLogic {
override def emailExists(emailId: String): Boolean = EmployeeQuery().emailId.is(emailId).exists
}
- Code should compile successfully.
# Implement command set code
- Open
EmployeeCommandSetCode.scalain intelliJ - Implement registerEmployee command to raise an event
import com.metastay.learningstream.stream.EmployeeRegistered
class EmployeeCommandSetCode(domainLogicRef: DomainLogicRef) extends EmployeeCommandSetCommands {
override def registerEmployee = RegisterEmployeeCommand {
import RegisterEmployeeCommand._
input: Input =>
val employeeId = new Id
val event = EmployeeRegistered(
employeeId = employeeId,
name = input.name,
gender = input.gender,
experienceInMonths = input.experienceInMonths,
designation = input.designation.id,
emailId = input.emailId
)
EventRaised(registered = event) -> Output(employeeId = employeeId)
}
}
- Code should compile successfully.
# Expose the command as a web api in play module
- Open LearningWeb.kplay file in eclipse *Define a web-writer for Employee & expose the above api as an action
web-writer Employee {
command-action registerEmlpoyee (POST) LearningDomain::Employee.registerEmployee
}
- Compile & run server to access the api.
- Now you can register an employee through web-api from swagger
# Write some unit tests to test the command using the command fixtures.
- Open RegisterEmployeeCommandTestSuite.scala file in intelliJ
- Write a test to see if the right event is getting raised (positive-test-case)
class RegisterEmployeeCommandTestSuite extends FunSuite with SmilePerTest {
override def beforeEach(testData: TestData): Unit = {
super.beforeEach(testData)
EmployeeWriter().drop()
}
test("register Employee", Tag("register"), ptest) {
grab[RegisterEmployeeCommandFixture]
.given()
.when(Input(name = "John", gender = "M", experienceInMonths = 10, designation = DesignationType.SE, emailId = "john@gmail.com"))
.expectEventRaisedMatch("name must match")(e => e.registered.name == "John")
.expectEventRaisedMatch("email id must match")(e => e.registered.emailId == "john@gmail.com")
}
}
- Write a test to ensure the pre-conditions work (negative test)
test("re-register an Employee", Tag("re-register"), ntest) {
grab[RegisterEmployeeCommandFixture]
.given(EmployeeRegistered(employeeId= new Id, name = "John123", gender = "M", experienceInMonths = 10, emailId = "john@gmail.com", designation = DesignationType.SE.id))
.when(Input(name = "John", gender = "M", experienceInMonths = 101,designation = DesignationType.SE, emailId = "john@gmail.com"))
.expectPreFail("emailIdMustBeUnique")
}
# Exercise: add the second employee (ptest)
# Read-side Story
# Define the read apis in a play module.
Ex: getEmployeeDetails, listAllEmployees(companyName)
- Open
LearningWeb.kplayfile in eclipse
web-reader Employee {
view getEmployeeDetails (GET) {
input(employeeId:Id)
output(LearningData::Employee)
}
view listAllEmployees (GET) {
input(companyName:String)
output(employeeList: LearningData::Employee*)
}
}
- Compile the code.
- Inorder to implement these 2 apis you will need to define the readDb Design readDb as per the client’s read requirement. Create a separate mongo module for this.
- Open
Mould.ksmilefile and add a new mongo module for readDb
mongo-module LearningReadDb(LearningData) at com.metastay.learningreaddb
- Run smile command & open LearningReadDb.kmongo file and define the read collection as follows:
collection Employee {
property name:String
property gender:String
property yearOfJoining:Int
property designation:LearningData::DesignationType
property experienceInMonths:Int
property emailId:String
reference company:Company
}
collection Company extend {
property name:String
property address:String
}
- Code should compile fine.
- Now list the events that would be needed to populate the read db under the projector inside the query module.
# Create a query module
- Add a query module in
Mould.ksmile
Now list the events that would be needed to populate the read db under the projector inside the query module.
query-module LearningQuery(LearningStream, LearningReadDb
) at com.metastay.learningquery
- Run smile command
- Open
LearningQuery.kqueryin eclipse, define the projector & the interested events
projector [LearningStream] Employee {
EmployeeRegistered
}
- Compile and you can code the projection logic in
EmployeeProjectorCode.scalato read from LearningReadDb collections
object EmployeeProjectorCode extends EmployeeProjector.Group {
override def alreadyProjected(context: EventContext): Boolean = false
override def handleException(event: LearningStreamEvent, context: EventContext, throwable: Throwable): DownstreamEHStrategy =
DownstreamEHStrategy.Stop
override def project(event: EmployeeRegistered, context: EventContext): Unit = {
val row = EmployeeRow(
_id = event.employeeId,
name = event.name,
gender = event.gender,
yearOfJoining = context.timestamp.toCalendarDateIndia.year,
experienceInMonths = event.experienceInMonths,
designation = DesignationType.withId(event.designation),
emailId = event.emailId
)
EmployeeWriter().insert(row)
}
}
- Compile
- Now run the server, invoke the registerEmployee api to add a new employee and you should see the employee collection of LeaningReadDb also populated.
# Implement the web reader
- Before that add the LearningReadDb module dependency to LearningWeb module in ksmile. Run smile command.
- Open EmployeeWebReaderCode.scala in intelliJ and implement getEmployeeDetails api
override def getEmployeeDetails: Request[GetEmployeeDetailsView.Pre] => com.metastay.learningdata.data.Employee = GetEmployeeDetailsView {
import GetEmployeeDetailsView._
request: Request[Input] =>
val input = request.body
EmployeeQuery.findById(input.employeeId).map(
row =>
new Employee(
name = row.name,
gender = row.gender,
yearOfJoining = row.yearOfJoining,
designation = row.designation,
experienceInMonths = row.experienceInMonths,
emailId = row.emailId.option
)
).get
}
- Run server and try out the api from swagger.
- Optionally define query-logic function if you need pre-conditions for read apis inside the query module. These functions will read from the readDb.
- Open
LearningQuery.kqueryfile in eclipse - Define a query-logic for Employee and define a predicate idExists which will be used in the pre-condition of getEmployeeDetails api
query-logic Employee {
function idExists(employeeId:Id):Boolean
}
- Compile
- Implement the query-logic code in
EmployeeQueryLogicCode.scala
class EmployeeQueryLogicCode extends EmployeeQueryLogic {
override def idExists(employeeId: Id): Boolean = EmployeeQuery.idExists(employeeId)
}
- Define the pre-condition in LearningWeb.kplay
- This will need a dependency of Query module to Web module in ksmile file
play-module LearningWeb(LearningDomain, LearningQuery, LearningReadDb) at learningweb
- Open
LearningWeb.kplayand add the following
web-reader Employee {
query-logic-ref employeeQLogicRef:LearningQuery::Employee
view getEmployeeDetails (GET) {
input(employeeId:Id)
pre {
condition idMustExist => q.employeeQLogicRef.idExists(input.employeeId)
failing "Employee Id does not exist"
}
output(LearningData::Employee)
}
- Compile
- Try to look up an invalid id in swagger to see this condition. Assignment - implement listAllEmployees api given a company name. (not as easy as it appears)
# Inside story
Current sequence number: Stream writer’s counter for event number
You can find this counter value in event-store db’s Stream-counter collection - a row with _id <streamModuleName>Stream ex: LearningStream as shown below
To read this number from command line execute the command streamDetails inside the stream module
[Mould] $ LearningStream/streamDetails
Stream : LearningStream
No of Events : 1
Stable SeqNo : 1
Highest SeqNo : 1
Lowest SeqNo : 1
Resolve Update counter : 0
# Stable number:
Stream writer updates the stable number when it has successfully written a group of related-events (originating from one command)
You can find this counter value in event-store db’s Stream-counter collection - a row with _id <streamModuleName>Stream-stable ex: LearningStream-stable as shown above.
To read this number from command line execute the command streamDetails inside the stream module
Projection writers update the projection based on this number and not counter.
# Projection writer:
The actor responsible for updating projection i.e. looking up events and executing the respective projection code.
The projection actor keeps its pointer (i.e. event number projected so far) in a database called snapshot-store inside collection <querymodulename> -snapshot-entry
Each projector has an entry in this collection.View field contains the projector name and seqNo is the event number that has been projected so far.
To read this number from command line execute the command projectionDetails inside the query module
[Mould] $ LearningQuery/projectionDetails
Employee -> Stable: 1, Projected: 1 -> UP-TO-DATE
# Running a projection
- In order to run a projection use the command projectionUpdate
- Takes the projectionName & till sequence number as input
[Mould] $ project LearningQuery
[LearningQuery] projectionUpdate Employee 10
# Re-running a projection
- Ensure your readDb is in a state for a re-run
- Clear or set the snapshot number appropriately, for example to run from the beginning you need to reset the snapshot number :
[LearningQuery] projectionSnapshotDelete Employee
[LearningQuery] projectionSnapshotCreate Employee 0
- Ensure the snapshot has been reset
[Mould] $ LearningQuery/projectionDetails
Employee -> Stable: 1, Projected: 0
- Now update the projection till the number you wish to run until
[LearningQuery] projectionUpdate Employee 10
